a way to solve minimization problem
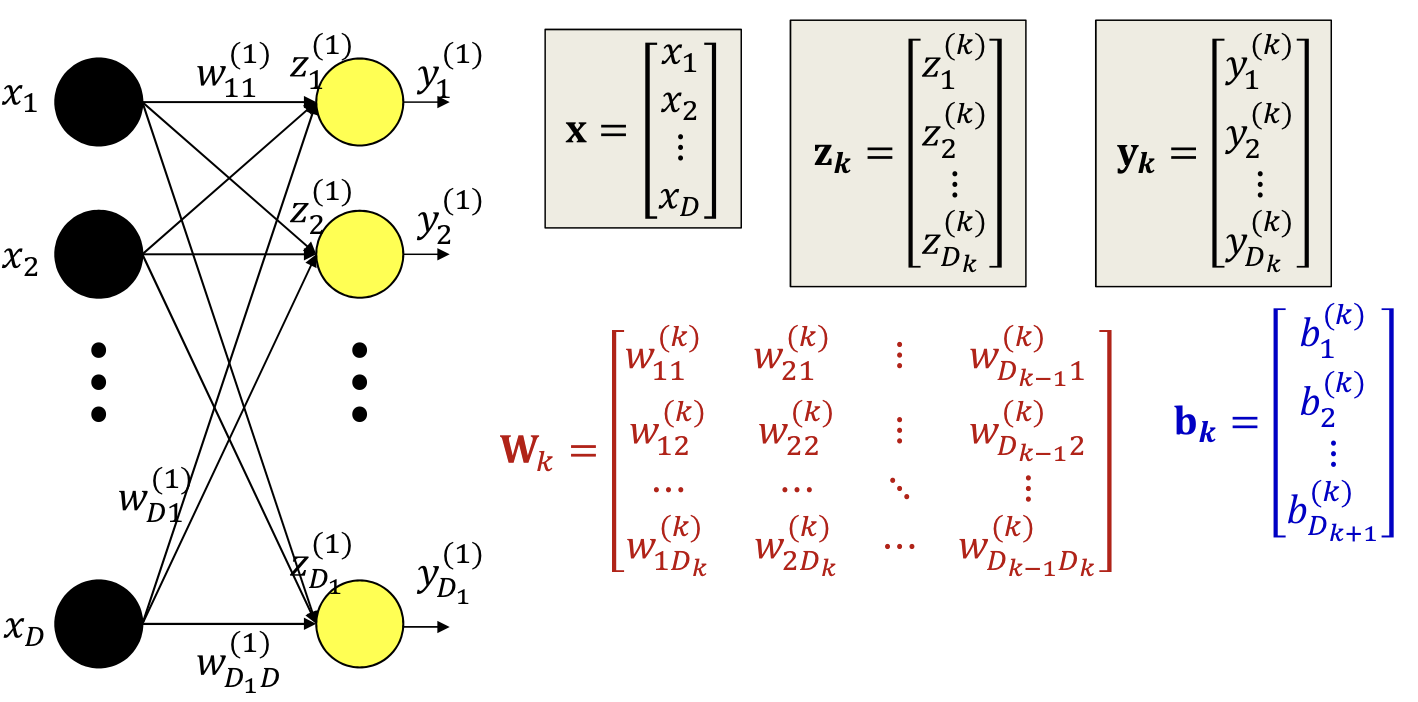
Problem setup
Input-output pairs: not to mention
Representing the output: one-hot vector
Divergence: must be differentiable
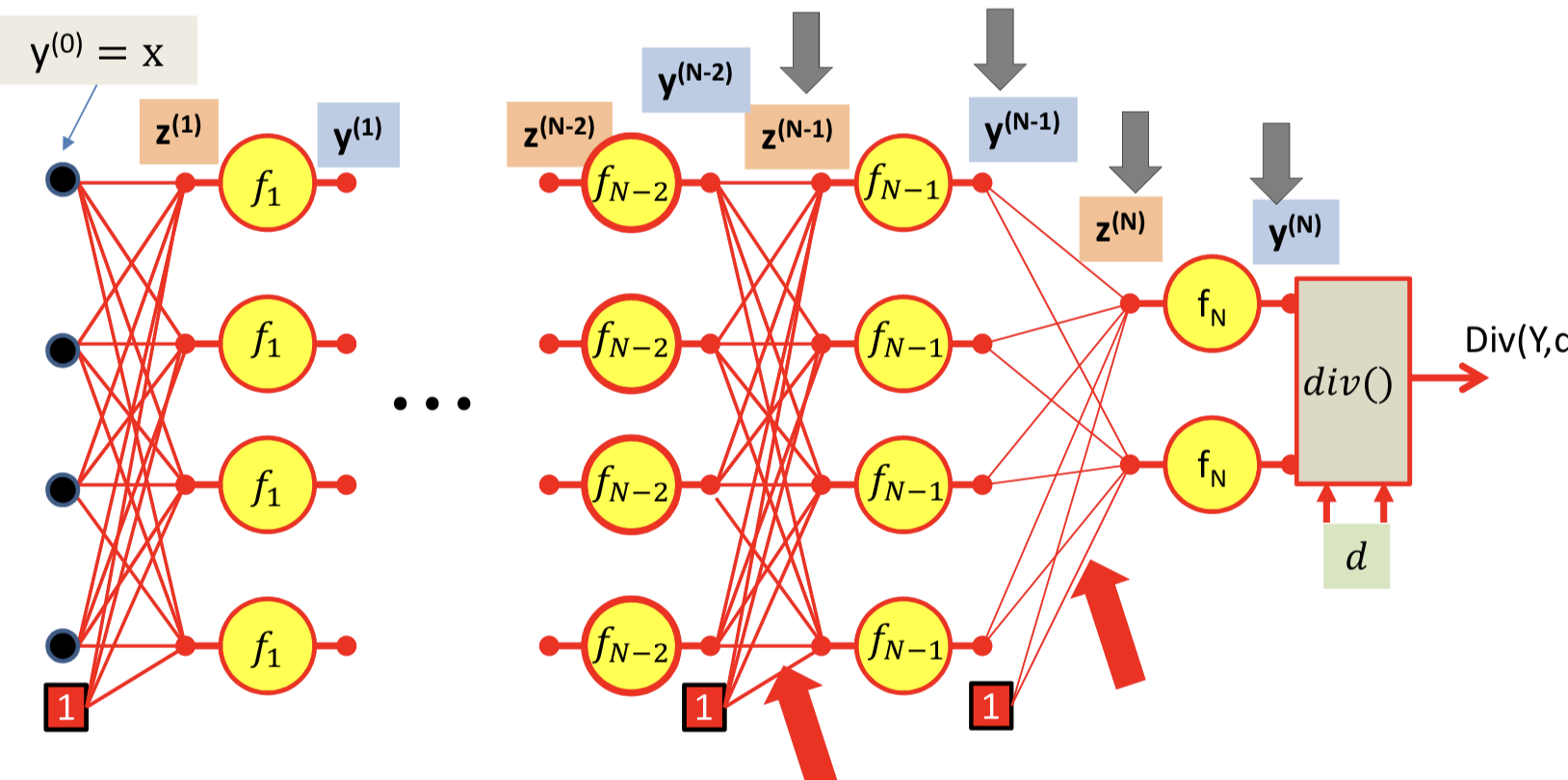
Train the network
Distributed Chain rule
y=f(g1(x),g1(x),…,gM(x))
dxdy=∂g1(x)∂fdxdg1(x)+∂g2(x)∂fdxdg2(x)+⋯+∂gM(x)∂fdxdgM(x)
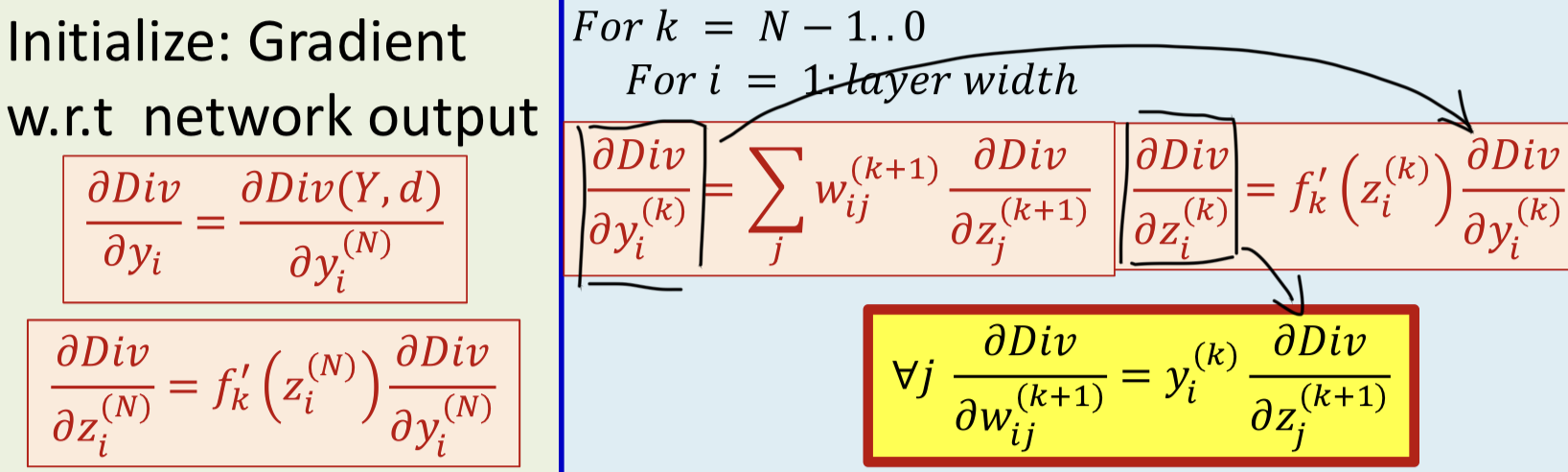
Backpropagation

Special case
Vector activations
- Vector activations: all outputs are functions of all inputs
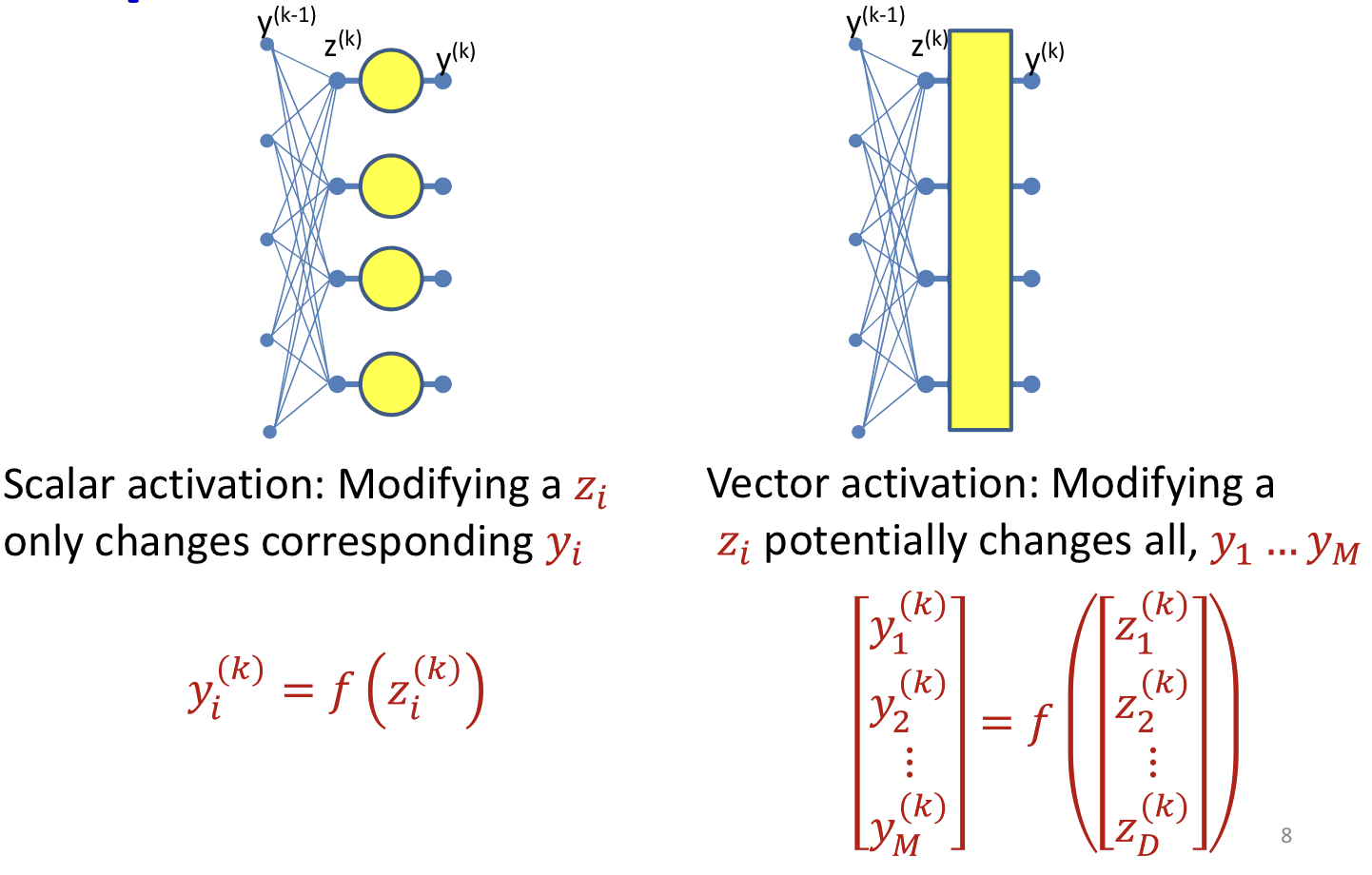
So the derivatives need to change a little
∂zi(k)∂Div=j∑∂yj(k)∂Div∂zi(k)∂yj(k)
Note: derivatives of scalar activations are just a special case of vector activations:
∂zi(k)∂yj(k)=0 for i≠j
For example, Softmax:
yi(k)=∑jexp(zj(k))exp(zi(k))
∂zi(k)∂Div=j∑∂yj(k)∂Div∂zi(k)∂yj(k)
∂zi(k)∂yj(k)={yi(k)(1−yi(k)) if i=j−yi(k)yj(k) if i≠j
- Using Keonecker delta δij=1 if i=j,0 if i≠j
∂zi(k)∂Div=j∑∂yj(k)∂Divyi(k)(δij−yj(k))
Multiplicative networks
- Some types of networks have multiplicative combination(instead of additive combination)
- Seen in networks such as LSTMs, GRUs, attention models, etc.
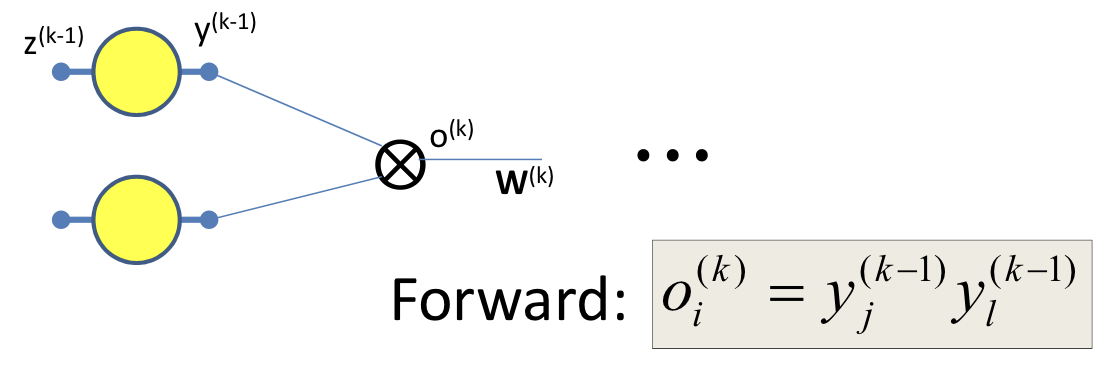
- So the derivatives need to change
∂oi(k)∂Div=j∑wij(k+1)∂zj(k+1)∂Div
∂yj(k−1)∂Div=∂yj(k−1)∂oi(k)∂oi(k)∂Div=yl(k−1)∂oi(k)∂Div
- A layer of multiplicative combination is a special case of vector activation
Non-differentiable activations
Forward pass

Backward pass
- Chain rule
- y=f(g(x))
- Let z=g(x),y=f(z)
- So Jy(x)=Jy(z)Jz(x)
- For scalar functions:
- D=f(Wy+b)
- Let z=Wy+b, D=f(z)
- ∇xD=∇z(D)Jz(x)
- So for backward process
- ∇ZNDiv=∇YDiv∇ZNY
- ∇yN−1Div=∇ZNDiv∇yN−1zN
- ∇WNDiv=yN−1∇ZNDiv
- ∇bNDiv=∇ZNDiv
- For each layer
- First compute ∇yDiv
- Then compute ∇zDiv
- Finally ∇WDiv, ∇bDiv
Training
Analogy to forward pass








